Peninsula Clean Energy Enters First Solar-Plus-Storage Power Purchase Agreement
October 1, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
October 1, 2021
California community choice aggregator (CCA) Peninsula Clean Energy and Leeward Renewable Energy have entered into a 15-year solar-plus-storage power purchase agreement (PPA) tied to Leeward’s 102-megawatt (MW) Chaparral Solar Facility in Kern County, California.
As part of the agreement, Redwood, Calif.-based Peninsula Clean Energy will also purchase the energy and capacity from Chaparral’s 52 MW (208 megawatt-hour) battery storage system.
Peninsula Clean Energy’s board of directors on September 25 approved the PPA, which is the organization’s first to involve a solar-plus-storage project. The CCA said that the Chaparral project will allow Peninsula Clean Energy to take another step toward its goal of delivering 100 percent renewable energy generation to its customers across San Mateo County and the City of Los Banos, Calif.
Construction of the facility will begin in December 2021 and the project is expected to begin delivering energy to Peninsula Clean Energy by December 2023. Leeward will own and operate the facility.
Peninsula Clean Energy is the official electricity provider for San Mateo County and, beginning in 2022, for the City of Los Banos. Founded in 2016, the agency serves 295,000 customers.
Peninsula Clean Energy is on track to deliver electricity that is 100 percent renewable by 2025 and has earned investment grade credit ratings from Moody’s and Fitch.
The American Public Power Association has initiated a new category of membership for community choice aggregation programs.
Additional information about Leeward is available here.
APPA To Assist Public Power Utilities With Energy Storage Under DOE Funding
September 29, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 29, 2021
The American Public Power Association (APPA) will bring together public power utilities to facilitate discussion, evaluate opportunities, and define barriers to integrating energy storage technologies with power plants thanks to funding it has received from the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Fossil Energy and Carbon Management (FECM). APPA will also work with DOE and other stakeholders to mitigate these barriers.
The cooperative agreement issued with the award “will support the development of tools, educational resources and training in long-term planning and policy analysis to improve the conditions of frontline communities impacted by the legacy of fossil fuel use and support a healthy transition to a clean energy economy,” DOE said.
APPA will also develop educational resources, publications and technical tools for public power utilities that will enhance their ability to explore and implement energy storage projects. “This work will directly benefit public power utilities, as well as the customers and communities that rely on them to ensure regional grid stability,” DOE noted.
“Integration of new resources can be leveraged to enhance the resilience of a public power utility,” said Nathan Mitchell, Senior Director of Operations Programs at APPA. “Being knowledgeable and prepared for this energy transition will help position public power utilities to meet the needs of their customers with high resilience and low emission energy delivery systems.”
He noted that energy storage is a developing technology and some public power utilities have utilized it for the benefit of their city and customers.
For example, Sterling Municipal Light Department (SMLD) in Massachusetts in 2019 marked a major milestone related to the department’s two energy storage systems. In March of that year, SMLD celebrated over $1 million in avoided costs to the light department, thanks to the two systems.
APPA plans to utilize the lessons learned from these and other energy storage installations to inform the work of a new energy storage working group to analyze the feasibility of energy storage at fossil fuel plants to enhance resiliency and lower emissions. DOE will provide $100,000 per year for five years, while APPA will provide $25,000 of in-kind cost share per year for five years, for a total value of $625,000.
DOE’s National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL) will serve as the contracting authority for the cooperative agreement.
NREL, Partners Developing Facility To Test Storage-Renewables Technologies
September 28, 2021
by APPA News
September 28, 2021
With support from the Department of Energy’s Grid Modernization Laboratory Consortium, three national laboratories are developing a variable hybrid power plant with energy storage at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s (NREL) Flatirons Campus in Arvada, Colo.
NREL, with its partners, Idaho National Laboratory (INL) and Sandia National Laboratories, will use the FlexPower facility to test hybrid renewable energy.
“This research will help accelerate the adoption of utility-scale variable wind and [photovoltaic] resources by demonstrating how hybridization can smooth the transition to clean energy,” Vahan Gevorgian, NREL’s chief engineer, said in a statement. “For the power grid to economically and reliably integrate large amounts of variable renewable generation, it will require robust energy storage capabilities and a rethinking of the value renewable energy assets bring to the grid.”
The researchers’ underlying thesis is that combining renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar plants, with energy storage can transform those variable resources into fully dispatchable and flexible energy sources capable of operating in day-ahead and real-time energy markets and providing essential reliability and resiliency services to the grid.
The researchers plan to test their thesis with a variety of energy storage systems, including pumped storage hydropower, battery, hydrogen, flow battery, kinetic, and ultracapacitor energy storage. They will also focus on advanced control strategies and resource forecast techniques.
The aim is to be able to use sophisticated control systems to improve the dispatchability and availability of variable generation by taking advantage of the complementary nature of wind and solar resources and increasing capacity factors for renewable projects with minimum or no additional transmission buildup.
With improved forecasting, hybrid plants also should be able to participate in energy and ancillary services markets in the same way conventional generation plants do, NREL said.
The researchers also anticipate that by combining generation, storage, advanced controls, and improved forecasting, operators will be able to achieve economies of scale by sharing infrastructure as well as siting and permitting costs.
They also envision that such hybrid plants would be able to provide a spectrum of essential reliability services as well as new, evolving grid reliability services. As examples they cited self-black starts as well as power system black starts; operation in islanded mode; and participation in power system restoration schemes.
The FlexPower project will provide a test bed for companies and researchers to validate and demonstrate hybrid plant concepts and strategies. The research results will be freely accessible to all stakeholders in the form of public domain information and other assets.
“Hybrid renewable energy plants could introduce the national and global energy sectors to a new and potentially disruptive class of power systems,” Gevorgian said. “The result could be high-value grid services and a more secure and resilient power supply.”
RFP Seeks Partner To Develop Large-Scale Pumped Storage Project In California
September 26, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 26, 2021
The San Diego County Water Authority this month issued a request for proposals seeking a full-service private partner capable of developing a large-scale pumped energy storage project planned jointly by the Water Authority and the City of San Diego.
In July 2021, the San Vicente Energy Storage Facility received $18 million in the state budget signed by California Gov. Gavin Newsom, enough to advance the project through initial design, environmental reviews, and the federal licensing process.
The project could store 4,000 megawatt-hours per day of energy (500 megawatts of capacity for eight hours).
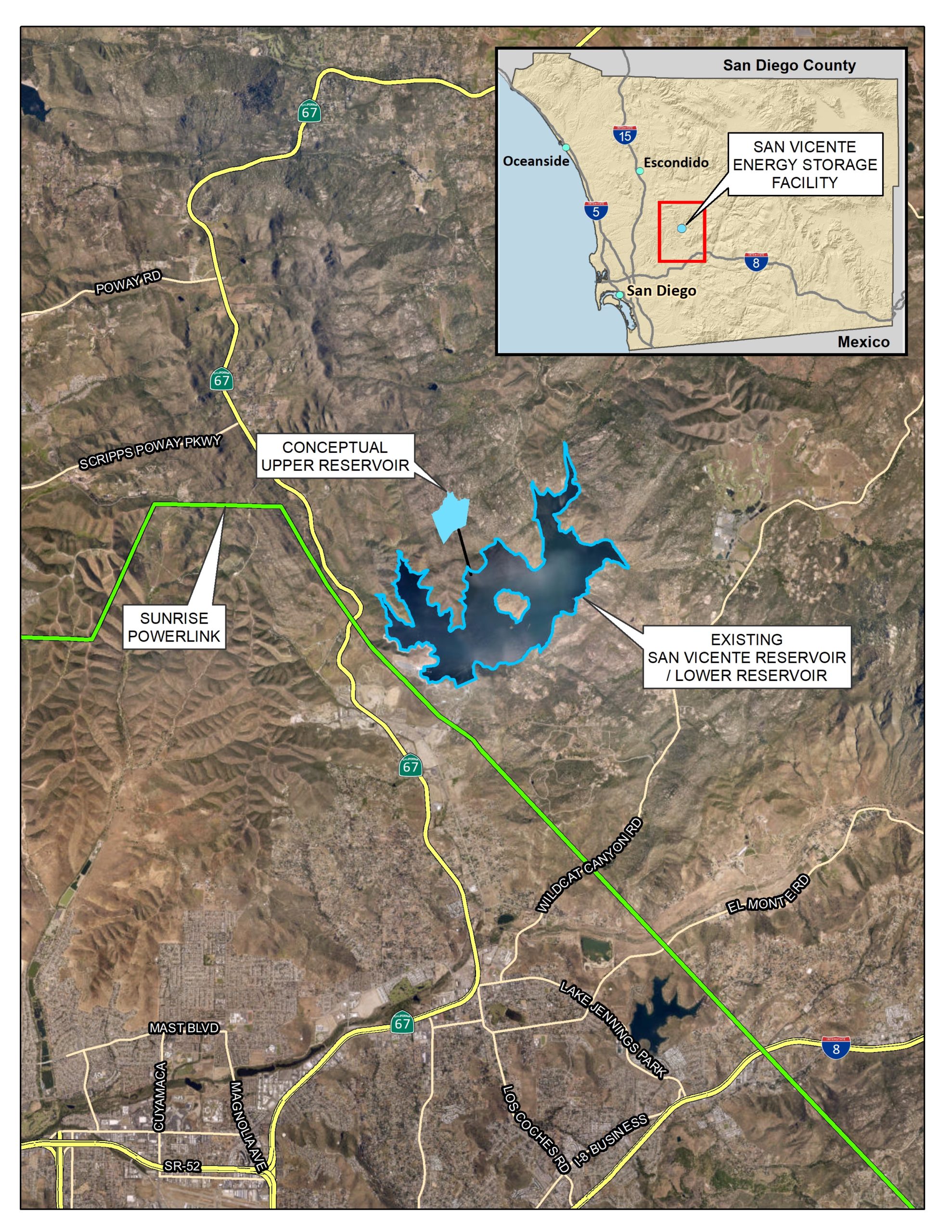
The potential project would create a small upper reservoir above the San Vicente Reservoir, along with a tunnel system and an underground powerhouse to connect the two reservoirs. The powerhouse would contain four reversible pump turbines.
The reservoir is near major electricity transmission interconnection facilities, which would allow the project to play a central role in integrating solar and wind energy from across the Southwest for use in San Diego County.
During off-peak periods, turbines would pump water to the upper reservoir where it would act as a battery of stored potential energy. During high energy use, the system would discharge energy as water from the upper reservoir flows downhill through the turbines. The exchange between the two reservoirs would not consume water and is closed-loop.
Proposals are due Nov. 3 and the RFP is available at: sdcwa.org/contracting-opportunities.
APPA Grant Helps CPS Energy Test Performance Of Energy Storage Solution
September 23, 2021
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
September 23, 2021
CPS Energy, the San Antonio, Texas, public power utility, has installed a project to test the performance of an energy storage system using a grant from the American Public Power Association’s Demonstration of Energy & Efficiency Developments (DEED) program.
CPS, with its partner, Yotta Energy, installed a small-scale applied technology project at the Joint Base San Antonio Fort Sam Houston Military Post. As part of the demonstration project, Yotta Energy will test the performance of its energy storage system in the Texas heat and its demand response features as a distributed energy resource (DER).
The DEED project will help CPS better understand how Yotta Energy’s renewable energy storage solution can lower costs for utility customers who elect to install distributed energy resources such as rooftop solar systems with battery storage by eliminating the need for onsite battery storage buildings while enabling the stabilization of an intermittent energy sources such as solar power.
The findings of the demonstration project will be used to provide insights on Yotta Energy’s integrated storage technology for CPS Energy. The performance data and feedback from the project will help Yotta make improvements to the features it offers in its forthcoming commercial product delivery, slated for early 2022, and for future commercial designs.
“CPS Energy is constantly searching for innovative technologies and proud to collaborate with Yotta Energy on this small-scale applied technology demonstration,” Frank Almaraz, chief power, sustainability and business development officer at CPS Energy, said in a statement. “The possibility of having a battery storage system attached to the actual solar panels excites us. It moves us one step closer to deploying cleaner, more resilient energy in our community that’s integrated and uses far less real estate.”
“We are excited to team up with CPS Energy, the largest public power company in San Antonio, to test and demonstrate the performance of our energy storage technology,” Omeed Badkoobeh, CEO of Yotta Energy, said in a statement. “Our team is also grateful for the grant funding from APPA because it will allow us to document, report, and validate our energy storage system’s performance under real-world conditions.”
CPS Energy is exploring a variety of alternative technologies, including energy storage solutions, as it deploys its Flexible Path resource plan that aims to move the San Antonio area to a decarbonized future by 2050 or sooner.
CPS Energy Signs MOU To Deploy Used EV Batteries For Storage
September 21, 2021
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
September 21, 2021
CPS Energy in San Antonio, Texas, has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to test recycled electric vehicle batteries to store energy produced by solar panels.
Under the MOU, signed with OCI Solar Power and Hyundai Motor Group, the parties aim to install an energy storage system. by September 2022. The storage system was developed by Hyundai, which is also providing the used, or “second life,” batteries at no cost. OCI Solar Power will procure some of the storage system components and supervise construction. CPS Energy will operate the storage system. All the partners will share data from the project.
After about seven or 10 years of use, a lithium-ion battery is no longer suitable to power an electric vehicle, but the battery still has enough capacity to be used in a stationary storage application.
Stationary storage powered by used electric vehicle batteries could exceed 200 gigawatt-hours (GWh) by 2030, according to a 2019 analysis by McKinsey & Co.
“We are taking a very important step in advancing our technology in regards to battery storage, thanks to this new collaboration with OCI Solar Power and the Hyundai Motor Group,” Fred Bonewell, chief operating officer at CPS Energy, said in a statement. “Evaluating these innovative technologies is key to discovering the next firming capacity that would be needed to replace fossil fuels.”
CPS Energy already has a 10 megawatt (MW), 1 hour duration battery storage system it installed about two years ago as part of a 5 MW solar facility. The $16.3 million project was done in partnership with the Southwest Research Institute, which provided the land.
The project aims to explore the potential for using batteries to shift solar power output to times when it is most needed on the grid. The solar-plus-storage project was also supported by a grant from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality.
At 500 kilowatts (kW), the newly announced project using second life batteries will be much smaller than the solar-storage project. And while it may connect to a CPS solar project eventually, the scope of the new project will likely be wider than solar shifting.
“We are calling it a small scale limited deployment project,” Jonathan Tijerina, senior director of business and economic development at CPS Energy, said. The battery system will likely do “a little bit of everything. We’ll try a lot of different scenarios,” he said, adding that the MOU is still in the early stages and one of the next steps will be to finalize the use cases for the new battery system.
The MOU will also evaluate the recycled batteries over the three to five year life of the project to assess how long the batteries can perform.
Late last year, CPS Energy issued a request for proposals to add up to 900 megawatts (MW) of solar, 50 MW of energy storage and 500 MW of firming capacity as part of its FlexPOWER Bundle initiative designed to replace some aging generation capacity and introduce new technologies as firming capacity to help ensure energy reliability for San Antonio.
The FlexPOWER program is part of CPS Energy’s broader Flexible Path resource plan that aims to move the San Antonio area to a decarbonized future by 2050 or sooner. The new second life battery project fits within the framework of CPS Energy’s Flexible Path plan, Tijerina said.
As of October 2020, CPS Energy had over 500 MW of solar power and more than 1,000 MW of wind power.
Salt River Project Brings 25-MW Battery System Online In Peoria, Ariz.
September 21, 2021
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
September 21, 2021
Salt River Project (SRP) has brought a 25-megawatt (MW), four-hour duration battery storage facility into operation at its Bolster substation next to its Agua Fria power plant in Peoria, Arizona.
The public power utility plans to charge the batteries at night when power prices are less expensive and discharge them during periods of peak energy demand.

“Battery storage is an extremely important and growing component of SRP’s 2035 Sustainability Goals to reduce our carbon footprint,” Kelly Barr, SRP’s chief strategy, corporate services and sustainability executive, said in a statement. “The Bolster Substation Battery System adds to our already considerable investment in battery storage and further allows us to offset carbon-emitting resources by storing energy and providing it to our customers when they need it most.”
The battery system consists of a series of Tesla Megapacks connected directly to SRP’s energy grid and is the largest stand-alone battery storage system in Arizona. SRP said the battery system’s renewable-charging capability will increase over time as it continues to add more solar energy resources to its grid.
This summer SRP announced an expanded commitment to add 2,025 MW of utility-scale solar energy by 2025.
Following that announcement, SRP in August announced three new solar plants that together will be capable of delivering 500 MW. Facebook will be the largest customer of the new facilities, taking 450 MW to support its newly announced data center in Mesa, Ariz., and to help meet the company’s 100 percent renewable energy commitments.
SRP recently contracted for the output from the Sonoran Energy Center, which would be the largest solar-charged battery project in Arizona and give SRP one of the largest commitments to energy storage in the nation. The utility has also contracted for the approximately 88-MW Storey solar and storage project to be built south of Coolidge. Both projects are scheduled to become operational in June 2023.
In addition to the new Bolster substation storage project, SRP receives power and collects data from two pilot battery storage projects: the Pinal Central Solar Energy Center, a 20 MW, integrated solar energy and battery storage plant in Casa Grande, and the Dorman battery storage system a 10 MW, 40 megawatt-hour stand-alone battery storage system in Chandler.
U.S. Storage Market Continued To Grow In The Second Quarter Of 2021
September 16, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 16, 2021
According to Wood Mackenzie and the U.S. Energy Storage Association’s (ESA) latest US Energy Storage Monitor report, 345 megawatts (MW) of new energy storage systems were brought online in the second quarter of 2021.
This is an increase of 162% over the same quarter in 2020, making the second quarter of 2021 the second-largest quarter on record by MW for U.S. energy storage additions. An unprecedented volume of storage will come online in in the second half of the year, with Wood Mackenzie expecting that storage projects representing over $5 billion of investment will come online in 2021 alone.
Details on the report were released on Sept. 9.
Despite positive market momentum in the U.S., the residential battery storage market dipped slightly, the first drop for the segment in nine quarters (since Q4 2018). Equipment constraints, including an ongoing Tesla Powerwall shortage, is hampering the segment’s growth despite the proliferation of new residential storage players, the report noted.
The non-residential segment, which consists of onsite storage and community-scale storage, saw quarter-on-quarter deployments rise by 31%, driven by the growth of the community storage market in Massachusetts.
The front-of-the-meter (FTM) market deployed 218 MW/729 megawatt hours (MWh) in Q2 2021, with California, Texas and Arizona leading the segment. California continued to lead the front-of-the-meter segment in Q2, with Arevon/Capital Dynamics’s 100MW/400MWh Saticoy Energy Storage peaker plant replacement in Ventura County, Calif., contributing most of the MW for the quarter. Solar-plus-storage projects in Texas and Arizona also bolstered Q2 front-of-the meter capacity.
Meanwhile, policy support continued to build in Q2, with several new state incentives introduced for residential and non-residential storage. The industry also still awaits the outcome of budget reconciliation, expected this winter, which could include a solar investment tac credit (ITC) extension and/or standalone storage ITC. A positive outcome would upgrade the energy forecast across all segments, Wood Mackenzie and ESA said.
Blue Ridge Power Agency Issues Battery Energy Storage System Request for Proposals
September 16, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 16, 2021
Virginia-based Blue Ridge Power Agency (BRPA) has issued a request for proposals (RFP) in which the joint action agency seeks pricing for several battery energy storage system (BESS) configurations that will aggregate to form a portfolio of BESS assets.
BRPA members are non-profit entities from six municipalities, towns, two cooperatives, and a university located in Virginia, each of which owns and operates its public power electric distribution system.
There will be four member projects participating in the RFP for this BRPA portfolio. The locations in the RFP will be strategically spread out across four members to capture benefits from BRPA’s member demand side management (DSM) activities.
The BESS sites are contemplated to be at locations provided by Craig Botetourt Electric Cooperative in Virginia, City of Radford, Va., City of Salem, Va., and Virginia Tech Electrical Services.
BRPA is seeking competitive proposals for a BESS to support BRPA’s DSM activities.
As outlined in the RFP, BRPA is looking for pricing for several BESS system configurations (2, 5, and 10 megawatt capacity ratings) that will aggregate to form a portfolio of BESS assets.
BRPA intends to select these configurations based on site-specific costs and project evaluation criteria. Commercial operation for the BESS is scheduled for June 2023.
Potential respondents can request the RFP and other information by contacting BRPA’s consultant, GDS Associates, Inc. Questions concerning the RFP should be directed to the following email address: BRPA.2021BatteryRFP@gdsassociates.com
Proposals in response to the RFP are due Nov. 1, 2021.
The American Public Power Association’s Public Power Energy Storage Tracker is a resource for association members that summarizes energy storage projects undertaken by members that are currently online.
Overheating Incident Takes 300-MW California Storage Facility Out Of Service
September 11, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 11, 2021
Vistra on Sept. 7 said that it has begun a preliminary assessment of Phase I of its Moss Landing energy storage facility in California following an overheating incident that impacted a limited number of battery modules and occurred on the evening of Sept. 4.
Phase I of the Moss Landing facility is a 300-megawat (MW)/1,200-megawatt hour (MWh) system and is out of service, while Phase II of the facility (100 MW/400-MWh), which is located in a separate stand-alone building, remains operational.
In the wake of the overheating incident, teams from Vistra, battery manufacturer LG Energy Solution, engineering and construction firm Fluence, and other external experts were conducting initial walkthroughs of the building in order to gather information and begin their investigation into the root cause of the issue. The North County Fire Protection District of Monterey County is assisting with the investigation.
The teams are in the early stages of this investigation and expect that it will take some time to fully assess the extent of the damage before developing a plan to safely repair and return the battery system to operation. “We are working with our partners to ensure all necessary safety precautions are in place to minimize any risk during this process,” Vistra said.
On Sept. 5, Vistra said that there are multiple layers of safety integrated into the battery facility and the risk mitigation and safety systems worked as designed, detecting these modules were operating at a temperature above operational standards and triggering targeted sprinkler systems aimed at the affected modules. As a result, the overheating was controlled and contained without the need for outside assistance.
“However, consistent with Vistra’s incident response planning and out of an abundance of caution, the Moss Landing team did ask the local fire department, North County Fire Protection District of Monterey County, to respond to the site. Importantly, there were no injuries to the facilities’ workers as a result of the incident and the situation is contained to the facility with no harm to the community,” the company said.
The 100-MW/400-MWh Phase II expansion is operating under a 10-year resource adequacy agreement with investor-owned Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E). The Phase I project has a similar 20-year resource adequacy agreement with PG&E.
The Phase II expansion project was completed in July 2021.
Vistra is an integrated retail electricity and power generation company based in Irving, Texas. According to the company, it is the largest competitive power generator in the U.S. with a capacity of approximately 39,000 MW powered by a portfolio that includes natural gas, nuclear, solar, and battery energy storage facilities.
