FERC And NERC Offer Recommendations In Preliminary Report On Cold Weather Event
September 29, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 29, 2021
Staff from the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) and the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) recently provided a report that includes preliminary findings and recommendations related to the February 2021 cold weather event that impacted the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT), Southwest Power Pool (SPP), Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO), and other regions.
FERC and NERC staff offered details on the report at FERC’s monthly meeting on Sept. 23.
The report reviews what happened during the freeze and outlines a series of recommendations, including mandatory electric reliability standards, to prevent its recurrence.
Following the staff presentation, FERC Chairman Richard Glick noted that 2011 FERC/NERC report released after a prior cold weather event that recommended mandatory weatherization requirements for electric generation facilities.
“But somehow that recommendation was eventually watered down to guidelines that few generators actually followed,” he said.
“Today’s report again recommends that generation facilities be required to winterize with a number of specific related recommendations,” Glick noted.
“I guarantee you that this time FERC will not permit these recommendations to be ignored or watered down,” he said.
Glick also said that it is “becoming increasingly apparent that electric grid reliability depends heavily on the reliability of natural gas production and delivery systems.”
Noting that the electric sector has been operating under a mandatory reliability regime since 2005, Glick said that “it is worth exploring whether additional actions may be necessary to enhance the reliability of the natural gas sector to address threats posed by both extreme weather and cyber or physical attacks to pipelines and other gas facilities.”
The February freeze triggered the loss of 61,800 megawatts of electric generation, as 1,045 individual generating units experienced 4,124 outages, derates or failures to start. It severely reduced natural gas production, with the largest effects felt in Texas, Oklahoma and Louisiana, where combined daily production declined to an estimated 20 billion cubic feet per day, FERC noted. That is a reduction of more than 50 percent compared to average production from February 1-5.
The FERC/NERC assessment points to freezing of generator components and fuel issues as the top two major causes of generator outages, derates or failures to start.
The identified causes in the preliminary report affected generating units across all fuel types. Of the 1,045 generating units affected, 57 percent were natural gas-fired units that primarily faced fuel-supply challenges.
What Went Right
In terms of what went right during the event, the preliminary report said that SPP, MISO and ERCOT reliability coordinators (RCs) coordinated and communicated well with each other.
It noted that beginning February 8, SPP and MISO begin management-level discussions about the upcoming severe cold weather forecast and natural gas fuel restrictions expected, and beginning February 14, they kept an open communication channel between control rooms throughout the event.
On Feb. 12, SPP began coordinating with ERCOT about which balancing authority would rely on switchable generation that both BAs depend on as capacity resources, the preliminary report went on to say.
“The RCs recognized that all three footprints were simultaneously having emergencies and cooperated to alleviate the most critical conditions first.”
Recommendations
The report offers 28 preliminary recommendations including nine key recommendations. Those key recommendations include changes to mandatory reliability standards that build upon the recently approved standards developed in the wake of a 2019 joint inquiry into a prior cold weather event.
The report also includes five preliminary recommendation areas for further study:
- Black start unit reliability;
- Additional ERCOT connections;
- Potential measures to address natural gas supply shortfalls;
- Potential effect of low-frequency events on generators in the Western and Eastern Interconnections; and
- Guidelines for identifying critical natural gas infrastructure loads
The recommendations also include proposed timeframes for implementation, most of which are either prior to Winter 2022/2023 or Winter 2023/2024.
The presentation of the preliminary findings and recommendations is available here.
The final report will be released in November.
San Francisco Public Utilities Commission Seeks Renewable Energy Supplies
September 29, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 29, 2021
The San Francisco Public Utilities Commission (SFPUC) is accepting bids for renewable energy supplies that will serve low-income CleanPowerSF customers in San Francisco.
Through a request for offers (RFO), the SFPUC is looking to purchase energy and associated capacity from new renewable energy resources located within the state’s disadvantaged communities (DACs).
These resources will serve two recently announced electricity discount programs that will be offered to eligible CleanPowerSF customers: the CleanPowerSF Disadvantaged Communities Green Tariff and the CleanPowerSF Community Solar Green Tariff.
The CleanPowerSF Disadvantaged Communities Green Tariff program is expected to begin serving customers in early 2022 with renewable energy from an already operating interim resource.
CleanPowerSF plans to transition participating customers to renewable energy produced by a new project located in Northern California as a result of the solicitation.
Eligible customers must live in a state-determined DAC in CleanPowerSF’s service area and must be low-income.
CleanPowerSF expects to serve approximately 1,200 customer accounts through the CleanPowerSF Disadvantaged Communities Green Tariff.
The CleanPowerSF Community Solar program will begin to serve customers by mid-decade. Eligible projects must be solar resources and located in a DAC that is within five miles of subscribing customers.
To be eligible to subscribe, customers must live in a DAC. At least 50 percent of the project’s capacity must be subscribed to by low-income customers, while the remaining 50 percent will be open to all DAC residents.
CleanPowerSF expects to serve about 350 customer accounts with the CleanPowerSF Community Solar Green Tariff program.
More information about the RFO is available at: www.cleanpowersf.org/energyvendors.
CleanPowerSF is a not-for-profit program of the SFPUC. California law allows cities and counties like San Francisco to pool the electricity demand of their residents and businesses, and purchase electricity on behalf of those customers. These programs are called community choice aggregation programs.
CleanPowerSF began serving customers in May 2016, giving residential and commercial electricity consumers in San Francisco the option to have more of their electricity supplied from renewable sources at competitive rates.
Officers Named For APPA’s Business And Financial section, Committees
September 29, 2021
by APPA News
September 29, 2021
New officers for the American Public Power Association’s (APPA) business and financial section and planning committees were named at the closing session of APPA’s 2021 Business & Financial Conference in Denver, Colorado.
Mel Palmer, Manager, Human Resources, Lincoln Electric System, Nebraska will chair APPA’s Business & Financial Section in 2021-2022. Andrew Fusco, Vice President, Member Services and Corporate Planning, ElectriCities of North Carolina is vice chair.
Joe Daggett, Director of Risk Management, WPPI Energy, Sun Prairie, Wisconsin will chair the Accounting & Finance Planning Committee; Laura Gutteridge Años, Manager, Financial Accounting & Reporting, JEA, Jacksonville, Florida will serve as vice chair.
Andrea Simmons, Manager of HR & Administration, Oklahoma Municipal Power Authority, Edmond, Oklahoma will chair the Human Resources Planning Committee and Patricia (Trish) Waugh, Business and Customer Care Manager, Stowe Electric Department, Vermont will serve as vice chair.
Julius Aubain, Chief Information Officer, Virgin Islands Water & Power Authority, St. Thomas, Virgin Islands will chair the Information Technology Planning Committee and Robin Britton, Chief Technology and Security Officer, New Braunfels Utilities, Texas will serve as vice chair. Tony Georgis, Managing Director, Energy Practices, NewGen Strategies & Solutions will serve as an advisory officer.
Carl Baker, Senior Electric Utility Analyst, Lakeland Electric, Florida will chair the Rates & Pricing Planning Committee; Chau Nguyen, Director of Analytical Services, Electric Cities of Georgia, Atlanta, Georgia will serve as vice chair.
Toni Hoang, Enterprise Risk Manager, SMUD, Sacramento, California will chair the Risk Management & Insurance Committee; Heath Silvey, Director – Risk Management, City Utilities of Springfield, Missouri will serve as vice chair.
APPA has been assessing the conference planning committees as part of a larger effort to assess how APPA can better serve its members. APPA will be adjusting some of the conference planning committees to better reflect current issues and to provide more robust programs to its members.
APPA will be combining the Customer Accounting & Services Planning Committee, which is currently part of the Business & Financial section, with the Customer Service Planning Committee, which is part of the Customer Connections section. Next year, the combined Customer Service Planning Committee will meet at the Customer Connections Conference.
For more information on the business and financial sections and committees, contact BusinessandFinance@PublicPower.org.
Salt River Project Unveils Plans For 400-MW Solar Plant
September 28, 2021
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
September 28, 2021
Arizona public power utility Salt River Project (SRP) has announced its largest standalone solar power project to date, a 400-megawatt (MW) facility scheduled to enter operation in 2024.
The CO Bar Solar project is sited on private land in Coconino County, Ariz. Clenara, a subsidiary of Enlight Renewable Energy, is contracted to build and operate the new solar plant. Construction is expected to begin in 2023 and to generate about 550 jobs, many of them local.
The project is the latest in a string of recent announcements aimed at supporting the public power utility’s long-term decarbonization goals.
In May, SRP said it would more than double its 2025 utility-scale solar commitment, raising the goal to 2,025 MW of utility-scale solar power that would be online by the end of fiscal year 2025.
In August, SRP announced three new solar energy plants capable of generating a total of 500 MW. The three projects include two 200-MW solar plants and a 100-MW solar facility. The first project is due online in fall 2022 and the other two will begin construction in 2022. Facebook has agreed to take 450 MW of the output of the projects.
With its commitment to add 2,025 MW of utility-scale solar resources by 2025 and its recent announcement of new solar projects, SRP anticipates that nearly 50 percent of the retail energy it delivers to customers will come from carbon-free resources by 2025, contributing to the utility’s goals to reduce carbon intensity by 65 percent in 2035 and by 90 percent in 2050 from 2005 levels.
SRP is also exploring the use of energy storage to help integrate intermittent solar resources into its grid with the recent announcement of a 25 MW battery storage facility at its Bolster substation as well as deals for solar-and-storage facilities scheduled to come online in June 2023.
NREL, Partners Developing Facility To Test Storage-Renewables Technologies
September 28, 2021
by APPA News
September 28, 2021
With support from the Department of Energy’s Grid Modernization Laboratory Consortium, three national laboratories are developing a variable hybrid power plant with energy storage at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s (NREL) Flatirons Campus in Arvada, Colo.
NREL, with its partners, Idaho National Laboratory (INL) and Sandia National Laboratories, will use the FlexPower facility to test hybrid renewable energy.
“This research will help accelerate the adoption of utility-scale variable wind and [photovoltaic] resources by demonstrating how hybridization can smooth the transition to clean energy,” Vahan Gevorgian, NREL’s chief engineer, said in a statement. “For the power grid to economically and reliably integrate large amounts of variable renewable generation, it will require robust energy storage capabilities and a rethinking of the value renewable energy assets bring to the grid.”
The researchers’ underlying thesis is that combining renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar plants, with energy storage can transform those variable resources into fully dispatchable and flexible energy sources capable of operating in day-ahead and real-time energy markets and providing essential reliability and resiliency services to the grid.
The researchers plan to test their thesis with a variety of energy storage systems, including pumped storage hydropower, battery, hydrogen, flow battery, kinetic, and ultracapacitor energy storage. They will also focus on advanced control strategies and resource forecast techniques.
The aim is to be able to use sophisticated control systems to improve the dispatchability and availability of variable generation by taking advantage of the complementary nature of wind and solar resources and increasing capacity factors for renewable projects with minimum or no additional transmission buildup.
With improved forecasting, hybrid plants also should be able to participate in energy and ancillary services markets in the same way conventional generation plants do, NREL said.
The researchers also anticipate that by combining generation, storage, advanced controls, and improved forecasting, operators will be able to achieve economies of scale by sharing infrastructure as well as siting and permitting costs.
They also envision that such hybrid plants would be able to provide a spectrum of essential reliability services as well as new, evolving grid reliability services. As examples they cited self-black starts as well as power system black starts; operation in islanded mode; and participation in power system restoration schemes.
The FlexPower project will provide a test bed for companies and researchers to validate and demonstrate hybrid plant concepts and strategies. The research results will be freely accessible to all stakeholders in the form of public domain information and other assets.
“Hybrid renewable energy plants could introduce the national and global energy sectors to a new and potentially disruptive class of power systems,” Gevorgian said. “The result could be high-value grid services and a more secure and resilient power supply.”
LIPA’s Board Approves PPA For 36-Megawatt Solar Farm
September 28, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 28, 2021
The Long Island Power Authority (LIPA) Board of Trustees on Sept. 22 approved a new power purchase agreement (PPA) for a 36-megawatt (MW) solar farm in Calverton, New York.
Once complete, this project will be the largest solar project on Long Island and among the largest throughout the state.
In 2015, LIPA and its service provider, PSEG Long Island, issued a request for proposals for new, renewable capacity and energy to expand LIPA’s portfolio of renewable energy resources.
In 2017, LIPA selected two solar farms for development — the 22.9 MW Riverhead Solar 1 with LI Solar Generation, LLC, which is currently under construction, and the 36 MW solar facility, which will be developed by a limited liability company owned by the AES Corporation and the Alberta Investment Management Company.
Riverhead Solar 2 will be adjacent to the existing Riverhead Solar 1 facility in Calverton. Both projects will be interconnected with the LIPA Edwards Avenue Substation. Since the project is larger than 25 MW, it underwent an extensive environmental review before approval by the LIPA Board and has met all applicable requirements.
LIPA will purchase all the capacity, energy, and renewable attributes produced by the project for 20 years and the commercial operation date is planned for June 1, 2023. The contract includes an option for LIPA to extend the term for an additional 10 years at a discounted price.
“Riverhead Solar 2 demonstrates the LIPA Board’s commitment to clean energy for Long Island and the Rockaways,” said LIPA CEO Tom Falcone in a statement. “Over the next five years, thousands of megawatts of new, clean energy projects will be connected to our local electric grid.”
DOE Offers Up To $16 Million To Assist Communities With Development Of Energy Plans
September 28, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 28, 2021
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) on Sept. 15 launched a pilot program that will provide supportive services valued at up to $16 million to help communities develop locally driven energy plans.
The Local Energy Action Program (Communities LEAP) program is available to assist to up to 36 low-income communities and energy-burdened communities “that are either experiencing environmental justice concerns or direct economic impacts from the shift away from historical reliance on fossil fuels,” DOE said.
Communities participating in Communities LEAP will develop an initial roadmap for identifying clean energy economic development pathways or accelerate progress toward existing plans for clean energy development projects.
Communities LEAP participants will receive support jointly offered by five DOE offices to pursue local energy action plans that focus on one or more of the following opportunities:
Creating Pathways For Large-Scale Clean Energy Project Planning And Infrastructure
Action plans can include design implementation and/or investment strategies for renewable energy projects that meet local environmental, economic, or community priorities and, where possible, quantifies benefits to community (e.g., energy bill savings, reduce pollution, improve energy access, revenue streams).
Among other activities, DOE anticipates providing selected communities with an analysis of clean energy planning and development opportunities based on current infrastructure, workforce availability, energy resource potential, utility regulatory structure. Projects could include technologies such as solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, hybrid power plants, energy storage, energy efficiency, distributed energy resources, and EV charging stations.
Evaluating The Ability To Use Microgrids To Increase Community Resilience
DOE will provide community partners with analysis and assistance to determine how they can install backup power under grid emergencies to ensure local critical facilities can maintain services for public health and safety and to keep a steady power supply available for local industries, businesses, and economic development zones.
Creating Job Opportunities In Fossil Fuel Communities Or Those Home To Heavy Industries
Action plans can evaluate Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) opportunities or develop a plan for energy site reclamation, critical mineral extraction, and/or create an environmental reclamation workforce program to train new or displaced workers that will assist in remediating environmental hazards from coal extraction and/or use.
Planning For Clean Transportation Investments
DOE’s partners will work with community stakeholders to assess the local transportation system, identify community transportation needs, and determine plan objectives (e.g., decarbonization, air quality improvement, community access to transportation, workforce development, increase electric vehicle charging availability, assess grid capacity for transportation electrification).
Improving Building Energy Efficiency
DOE’s technical assistance providers will work with community stakeholders to assess the current building stock and power supply, identify building-related load management needs and opportunities for energy and cost savings, and determine additional community priorities such as reducing energy bills for residents and businesses, increasing building and community resilience and sustainability, improving the health of indoor environments, and developing new workforce opportunities.
Enhancing Investments In The Clean Energy Supply Chain
Selected communities can receive assistance to engage with existing local manufacturing facilities on energy performance to lower emissions and reduce waste; identify how local strengths – such as natural resources or existing manufacturing infrastructure or capabilities – could play a role in manufacturing new clean energy technologies.
DOE is accepting comments until October 12 on the content of the opportunity announcement through emails addressed to: CommunitiesLEAPInfo@hq.doe.gov.
Applications are due December 17 and selections are expected to be announced in March 2022.
Additional information is available here.
BPA On Path To Join Western Energy Imbalance Market In March 2022
September 27, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 27, 2021
After more than three years of rigorous review and analysis, the Bonneville Power Administration (BPA) has decided to join the Western Energy Imbalance Market (EIM) in March 2022, BPA said on Sept. 27.
Participation in the California Independent System Operator’s (CAISO) Western EIM is expected to further enhance the value of the Northwest’s federal power and transmission system, BPA noted.
“This decision aligns with Bonneville’s strategic plan and opens up an opportunity to increase revenues through additional sales of surplus power and to reduce costs through greater efficiencies,” said BPA Administrator John Hairston in a statement. “As the West moves rapidly to decarbonize the grid, Western EIM participation will help us navigate future challenges and leverage opportunities to benefit our customers and the Northwest.”

BPA will now sign a Western EIM Entity Agreement as well as the remaining participation agreements with CAISO. CAISO will file the signed agreements with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission for approval. BPA plans to begin its final testing stage — parallel operations — on Dec. 1, 2021.
BPA is currently completing the work to implement new systems and processes to enable participation in the Western EIM beginning March 2022. The internal preparations are on-track and testing with the ISO has already begun.
Beginning in fall 2021, BPA will continue to hold implementation workshops to work through changes for customers, which will include informal and formal settlements training, and provide updates on BPA’s implementation efforts.
“Western EIM participation is a great introduction to emerging markets in the west,” said Hairston. “We hope to build on this experience to assess future market-based opportunities.”
As BPA assessed participation in the Western EIM, discussions about other industry improvements and market opportunities also emerged, BPA noted.
BPA plans to take part in the development of other markets and opportunities and will make decisions about its participation in these efforts through additional public processes.
One such opportunity is the Western Resource Adequacy Program organized by the Northwest Power Pool.
BPA proposed in a draft decision posted August 20 to participate in the next non-binding phase of this effort in which parties will test the design concepts, determine the program’s viability and shape its final design.
This is a first step at establishing common resource adequacy measurements and definitions.
In addition to participating in the Western Resource Adequacy Program, BPA is closely monitoring the potential formation of day-ahead markets in the West.
Both CAISO and Southwest Power Pool (SPP) have presented initial concepts that could provide additional opportunities and benefits for BPA and its customers, BPA said.
SPP manages the electric grid across 17 central and western U.S. states and provides energy services on a contract basis to customers in both the Eastern and Western Interconnections.
Information on BPA’s decision to join the Western EIM can be found at www.bpa.gov/goto/eim.
The Western EIM footprint currently includes portions of Arizona, California, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Oregon, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming, and extends to the border with Canada.
CAISO on Sept. 15 signed an implementation agreement with the Western Area Power Administration Desert Southwest region to participate in CAISO’s real-time energy market in 2023.
California Governor Signs Offshore Wind Legislation Into Law
September 27, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 27, 2021
California Gov. Gavin Newsom recently signed into law a bill that directs state agencies to develop a strategic plan for offshore wind resources in California.
Newsom on Sept. 23 signed into law AB 525 by Assemblymember David Chiu.
Under the new law, the California Energy Commission (CEC) has until June 1, 2022, to evaluate and quantify the maximum feasible capacity of offshore wind “to achieve reliability, ratepayer, employment, and decarbonization benefits and shall establish megawatt offshore wind planning goals for 2030 and 2045.”
The law also calls for the CEC, in coordination with the California Coastal Commission, Department of Fish and Wildlife, Ocean Protection Council, and State Lands Commission, to work with stakeholders, other state, local, and federal agencies, and the offshore wind energy industry to identify suitable sea space for wind energy areas in federal waters sufficient to accommodate the offshore wind planning goals.
In May 2021, the Biden administration, in conjunction with Newsom, announced an agreement identifying regions off the California coast that could support the administration’s goal of deploying 30 gigawatts (GW) of offshore wind energy by 2030.
According to a recent report, California has enough offshore wind power potential to meet 157% of the state’s 2019 electricity use.
RFP Seeks Partner To Develop Large-Scale Pumped Storage Project In California
September 26, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 26, 2021
The San Diego County Water Authority this month issued a request for proposals seeking a full-service private partner capable of developing a large-scale pumped energy storage project planned jointly by the Water Authority and the City of San Diego.
In July 2021, the San Vicente Energy Storage Facility received $18 million in the state budget signed by California Gov. Gavin Newsom, enough to advance the project through initial design, environmental reviews, and the federal licensing process.
The project could store 4,000 megawatt-hours per day of energy (500 megawatts of capacity for eight hours).
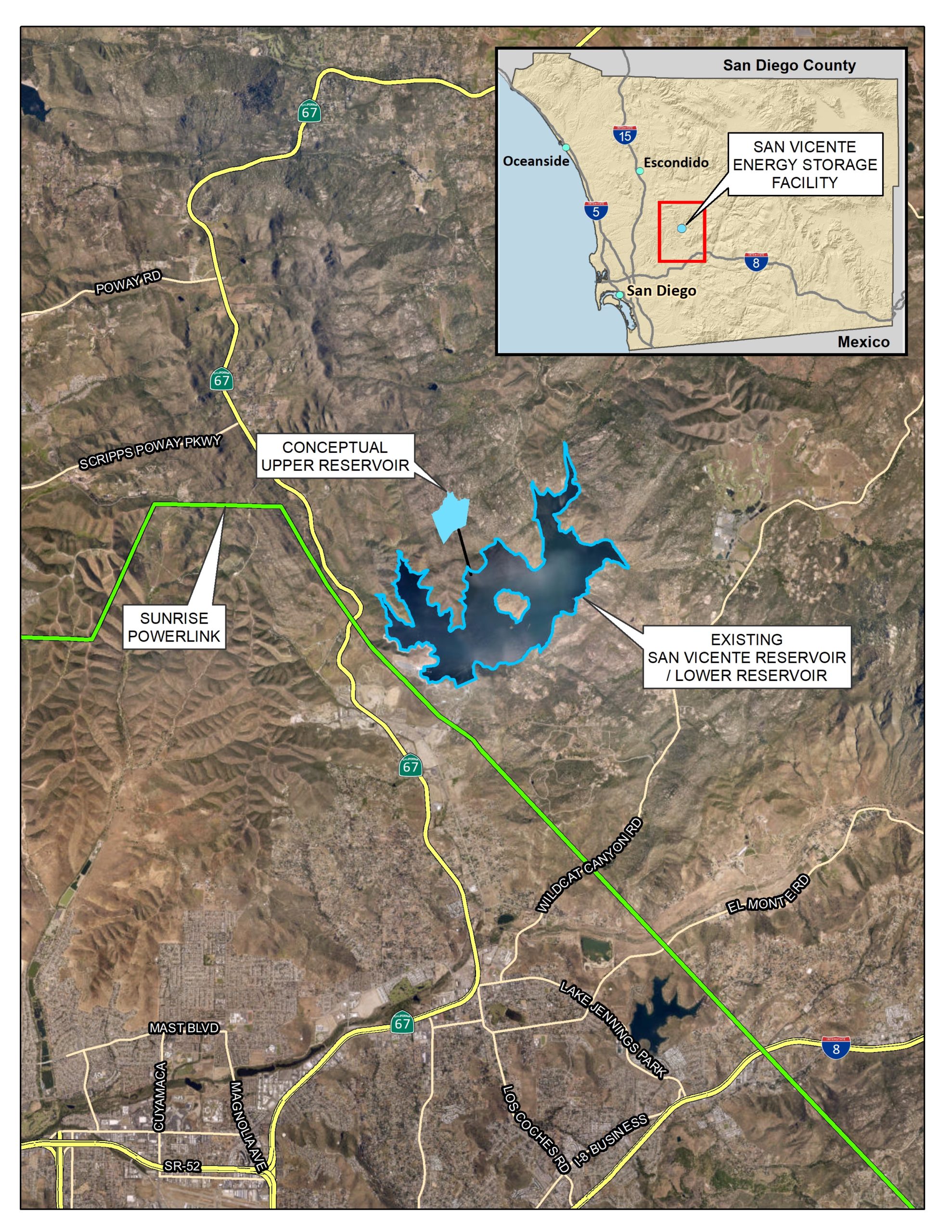
The potential project would create a small upper reservoir above the San Vicente Reservoir, along with a tunnel system and an underground powerhouse to connect the two reservoirs. The powerhouse would contain four reversible pump turbines.
The reservoir is near major electricity transmission interconnection facilities, which would allow the project to play a central role in integrating solar and wind energy from across the Southwest for use in San Diego County.
During off-peak periods, turbines would pump water to the upper reservoir where it would act as a battery of stored potential energy. During high energy use, the system would discharge energy as water from the upper reservoir flows downhill through the turbines. The exchange between the two reservoirs would not consume water and is closed-loop.
Proposals are due Nov. 3 and the RFP is available at: sdcwa.org/contracting-opportunities.
