U.S. Storage Market Sets New Installation Record In Q3 2021
December 12, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
December 12, 2021
The U.S. energy storage market set a new record in the third quarter of 2021, with new system installations totaling 3,515 megawatt hours (MWh).
Wood Mackenzie and the Energy Storage Association’s latest U.S. Energy Storage Monitor report, released Dec. 9, said with market momentum building, it is likely this storage market record will be broken in the fourth quarter.
In addition, an expected solar investment tax credit (ITC) extension, standalone storage ITC, and a California solar and storage mandate are all assumed in the forecast for the first time this quarter, significantly increasing forecast storage deployment.
The third quarter saw the utility-scale front-of-the-meter (FTM) market deploy 998 MW/3198 MWh, with California, Texas and Arizona leading the segment.
California continued to lead in FTM project deployment, with a trio of projects developed by NextEra Energy Resources near Blythe contributing the majority of the MW for the quarter. Storage projects in Texas developed by Broad Reach Power also boosted third quarter FTM capacity.
Installations increased slightly in the residential market as attachment rates continue to rise, with another 97.9 MW/225 MWh of new residential storage brought online in the quarter.
But project timelines for residential solar-plus-storage remain problematic, with solar module and battery constraints among the challenges contributing to project backlogs. However, vendors and installers managed to increase residential storage deployment over the second quarter.
The non-residential market recorded its best quarter of 2021 so far, with 43.6 MW/92.1 MWh deployed.
Commercial virtual net metered and community solar projects with storage attached contributed most of the non-residential capacity in the third quarter, with most behind-the-meter non-residential projects sited in California.
Peninsula Clean Energy Signs Wind Farm Power Purchase Agreement
December 11, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
December 11, 2021
Scout Clean Energy and California community choice aggregator (CCA) Peninsula Clean Energy have signed a 15-year Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) that will provide San Mateo County and City of Los Banos customers with 76.35 megawatts (MW) from the repowering of the Pacheco Pass Wind Farm in Merced County, Calif.
Construction will begin in late 2023 and the project will replace the existing 162-turbine wind farm in Pacheco State Park, originally built nearly four decades ago, with a much-smaller fleet of far more powerful state-of-the-art turbines that are expected to be operational by around the end of October 2024.
While the existing 162 turbines produce 16.5 MW, Scout is planning a total capacity of 147.5 MW of wind energy and a 50-MW four-hour Battery Energy Storage System. The completed project upgrades would be one of the first repower projects on state land in California.
GRWF will be located about 10 miles from the groundbreaking 200-MW Wright Solar Project, which in January 2020 became the largest renewable energy installation at the time ever built for a CCA to officially go online.
Wright Solar was Peninsula Clean Energy’s first project located in Merced County and California’s Central Valley.
Peninsula Clean Energy is the official electricity provider for San Mateo County and, beginning in 2022, for the City of Los Banos.
Founded in 2016, the agency serves 295,000 customers by providing more than 3,500 gigawatt hours annually of electricity.
The American Public Power Association has initiated a new category of membership for community choice aggregation programs.
LCRA Awards More Than $730,000 In Community Grants
December 11, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
December 11, 2021
The Lower Colorado River Authority (LCRA) recently awarded more than $730,000 in Community Development Partnership Program (CDPP) grants for a wide range of projects across LCRA’s wholesale electric, water and transmission service areas.
CDPP grants are awarded twice a year for capital projects for volunteer fire departments, emergency responders, cities and counties, schools, libraries, civic groups, museums, and other tax-exempt non-profit organizations.
The grants will help fund 32 community projects, including the purchase of a new firetruck for the Wall Volunteer Fire Department in Tom Green County and renovation of the Wharton Civic Center in Wharton County. Other grants will help fund a new public park alongside the Colorado River in Smithville; the construction of a live-fire training facility in Coleman; and the completion of renovations to public art galleries in downtown Llano.

LCRA serves customers and communities throughout Texas by managing the lower Colorado River, generating and transmitting electric power, providing a clean, reliable water supply and offering outdoor adventures at more than 40 parks along the Colorado River from the Texas Hill Country to the Gulf Coast. LCRA was created by the Texas Legislature in 1934 and receives no state appropriations.
LCRA noted in a Dec. 10 news release that fourteen of the projects will support first responders by providing new protective gear, emergency vehicles and other critical resources. One grant will help pay for a 40,000-gallon water tank that firefighters can use in the Spicewood area, where the nearest fire hydrants are several miles away. Another will provide a new thermal imaging camera and smoke evacuation fans to aid firefighters in Kerr County.
LCRA General Manager Phil Wilson said providing these grants to volunteer fire departments and other first responders is important to help keep communities safe.
“By helping supply new protective gear and better, up-to-date equipment, we can make it easier for first responders to get to emergencies quickly, with top-notch gear at their sides as they work to protect people who need help,” Wilson said.
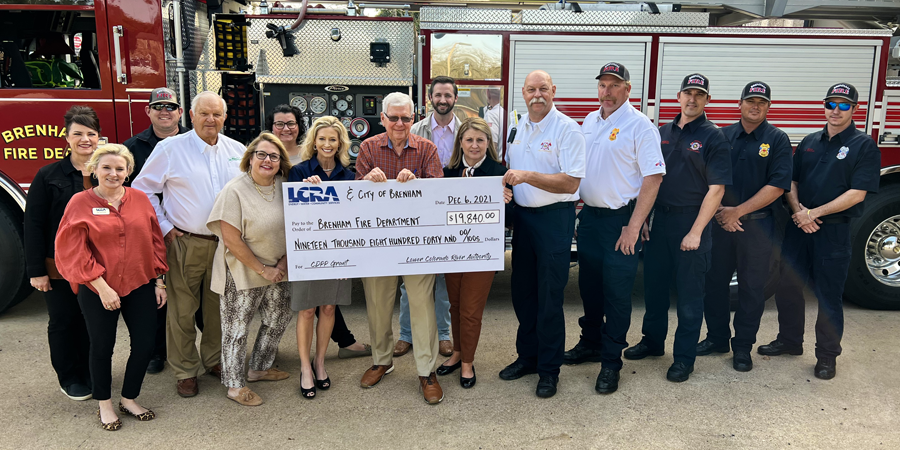

To date, LCRA and its wholesale electric customers have awarded 1,852 community grants totaling nearly $48 million. When combined with more than $228 million in community-raised matching funds, the program has invested more than $276 million in local communities.
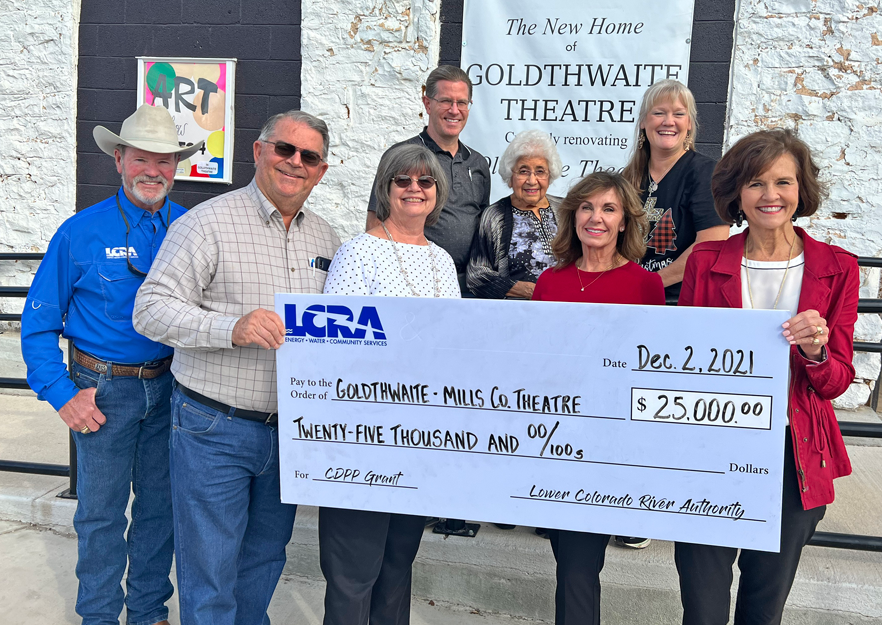

The complete list of the 32 grants awarded in the most recent grant cycle are available here.
Northern California Power Agency Installs EV Chargers At Its Headquarters
December 10, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
December 10, 2021
The Northern California Power Agency (NCPA) on Dec. 9 unveiled four new Level 2 electric vehicle (EV) charging stations at its headquarters facility in Roseville, Calif.
The chargers will be available for use by NCPA employees, members, and guests visiting the NCPA premises.
Each of the EV chargers has two ports, allowing up to eight vehicles to charge simultaneously.
The planning, preparation of the site, and installation of the chargers took place over the last 18 months.
Planning started in June 2020. A public works contractor was selected through a competitive process in November 2020 and permitting, construction, and installation of the chargers took place in 2021. The project was completed on Nov. 1, 2021.
In 2020, California Gov. Gavin Newsom issued Executive Order N–79–20, which set a goal of 100% of new light-duty vehicle sales to come from zero-emission vehicles by 2035, with similar goals for medium- and heavy-duty vehicles following ten years later.
NCPA members are encouraging the use of zero-emission vehicles in their communities, including in their fleets and installing new infrastructure to support state policy goals.
The project “is a demonstration of the strong commitment that both NCPA and the City of Roseville Electric Utility have to support transportation electrification as a means to reduce emissions in the local community,” NCPA said.
Roseville Electric provided critical funding and valuable technical support for the commercial installation, helping advance the project from a conceptual plan to a reality. Extending beyond the financial assistance, city staff helped NCPA navigate the permitting process and develop an alternative metering arrangement with the electric utility.
NCPA applied and received a funding reservation through the California Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Program (CALeVIP). The agency anticipates receiving a $28,000 incentive through the program.
CALeVIP is funded through a grant from the California Energy Commission’s Clean Transportation Program.
NCPA is a nonprofit California joint powers agency established in 1968 to construct and operate renewable and low-emitting generating facilities and assist in meeting the wholesale energy needs of its 16 members, which includes Roseville.
President Biden Signs Executive Order Directing Government To Procure Carbon Free Electricity
December 10, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
December 10, 2021
President Joseph Biden on Dec. 8 signed an executive order (EO) that directs the federal government to procure 100 percent carbon free electricity on a net annual basis by 2030.
The EO directs the federal government to make only zero-emission vehicle purchases by 2035, including 100 percent zero-emission cars and other light-duty vehicles by 2027. The order also directs the government to achieve a net-zero emissions building portfolio by 2045 and net-zero emissions from federal procurement no later than 2050.
There are also interim goals, including cutting greenhouse gas emissions from federal buildings in half by 2032 and from all federal operations by 65 percent by 2030.
OMB Memorandum
Shalanda Young, acting director of the White House Office of Management and Budget (OMB), issued an accompanying memorandum to agency leaders with instructions on implementing the EO that includes a list of deadlines and annual targets to ensure government-wide progress around the administration’s clean energy initiatives. The memo included annual requirements for agencies to submit updated strategic plans to achieve a zero-emission fleet of federal vehicles.
Additionally, the memo spells out the requirement for agencies to designate a senior official as chief sustainability officer within 30 days of issuing the order. That official should have “the authority to ensure allocation of resources to effectively implement the [executive order],” and will take responsibility for, among other activities, coordinating with leaders including chief information and chief financial and acquisition officers to achieve the policy goals of the executive order.
OMB also called on agencies to use data analytics while conducting capital planning and building retrofits to achieve the EO’s goal of a net-zero emissions building portfolio by 2045, and said plans must ensure fossil-fuel consuming equipment is required to be replaced with carbon pollution-free energy technologies.
Federal Government To Work With Utilities, Others
The federal government will work with utilities, developers, technology firms, financiers and others to purchase electricity produced from resources that generate no carbon emissions, including solar and wind, for all its operations by 2030.
Half of the federal government’s 100 percent carbon free annual electricity demand will be procured on a 24/7 basis.
“With the scope and scale of this electricity demand, the federal government expects it will catalyze the development of at least 10 gigawatts of new American clean electricity production by 2030,” the White House said in a news release.
The EO also addresses environmental justice, noting that ensuring economic equity and environmental justice are key considerations in operations planning and decision making.
The Council on Environmental Quality will issue guidance, as necessary, to implement the order, and among the principal agencies targeted for action under the EO are the Army Corps of Engineers, Department of Justice, Interior, Environmental Protection Agency, and Department of Energy.
Concepts in the EO, such as what it means to “buy clean” and how carbon pollution-free electricity is defined, could be more formally adopted through proposed rules.
The EO is available here.
Biden Signs Executive Order Aimed At Addressing Climate Change
Shortly after Biden took office, he vowed to use the power of the federal purse to help achieve his administration’s climate change goals, which includes a net-zero economy by 2050.
In January, Biden signed an EO aimed at addressing climate change that consists of two major parts, with the first part addressing foreign policy and national security and the second part focused on a domestic “government-wide” approach.
The executive order establishes the roles and responsibilities of both the Special Presidential Envoy for Climate, focused on international activities, and the National Climate Advisor, focused on domestic efforts.
It also creates a National Climate Task Force comprised of cabinet members and agency leaders. Those leaders will be tasked with, among other things, creating a federal clean electricity and vehicle procurement strategy that will use as available procurement authorities to achieve or facilitate “a carbon pollution-free electricity sector no later than 2035” and “clean and zero-emission vehicles for Federal, State, local, and Tribal government fleets.
ERCOT, Texas PUC Leaders Detail Actions Taken To Bolster Grid Reliability This Winter
December 9, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
December 9, 2021
Public Utilities Commission of Texas (PUCT) Chairman Peter Lake and Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) Interim President and CEO Brad Jones recently provided an update on grid operations and the actions their organizations are taking to improve grid reliability this winter.
At a press conference, Lake and Jones detailed the ongoing reforms and actions underway to ensure a stronger and safer grid, including:
- ERCOT will continue policies put in place this summer that operate the grid in a conservative manner with an abundance of power reserves;
- ERCOT’s Emergency Response System that allows large electric consumers to curtail their usage under direction from ERCOT can now be used before the grid encounters emergency conditions;
- The PUCT has reduced the cap on high prices that can be charged when supply is tightest, lowering the cap from $9,000 per megawatt hour (MWh) to $5,000 per MWh;
- Along with the Railroad Commission of Texas, the PUC has adopted a rule to designate natural gas facilities that are critical to the operation of the electric grid; and
- PUCT rules required the weatherization of power plants in Texas by December 1. This will be verified by ERCOT inspections of power plants
In addition, penalties for violating weatherization rules have increased to $1,000,000 per day per violation.
PUCT Staff Files Reports Of Violation Against Generation Companies
PUCT staff on Dec. 8 filed reports of violation against eight generation companies for failure to file winter weather readiness reports by the Dec. 1, 2021 deadline.
Out of the 850 generation resources in the state, PUCT’s Division of Compliance and Enforcement identified 13 separate generation resources owned by the eight companies that missed the deadline. These 13 resources have the ability to generate 801 megawatts of electricity out of the state’s total installed capacity of 120,000 MW, or less than one percent of the state’s total.
The winter weather readiness reports are critical to ensure the generation fleet in Texas is more prepared to provide service through severe winter weather, the PUCT Said. Failure to file winter weather readiness reports on time does not indicate whether or not these companies have taken the steps to weatherize their facilities. Subsequent inspections by ERCOT will verify that.
In October 2021, the PUCT adopted a new rule requiring power generators and electric transmission companies to take actions based on weather preparation best practices in advance of the 2021-2022winter season.
Entities receiving violations have 20 days to respond to the notice of violation and can request a hearing.
Grant PUD GM, CEO Kevin Nordt Steps Down Amid Battle With Prostate Cancer
December 9, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
December 9, 2021
Grant PUD General Manager and CEO Kevin Nordt stepped down on Dec. 6 to assume an important but less physically demanding role in helping assure a long-term power supply for Grant PUD customers, the PUD said on Dec. 2.
Nordt, 56, has undergone vigorous treatment for prostate cancer since he was diagnosed in June 2020, the Washington State PUD noted.

Grant PUD Chief Operations Officer Rich Wallen will become acting general manager through the balance of the year until commissioners decide on a longer-term appointment.
“I have responded well to my treatments but I also have seen my capabilities diminish significantly. This is no surprise; just part of the deal,” Nordt said in a statement. “I have now come to the realization that my health no longer allows me to function in the role of general manager/CEO at the level our employees and the people of Grant County deserve. Rich Wallen is a skilled and wonderful fellow. I will do everything I can to make he and Grant PUD successful, going forward,” he said.

Nordt will take on the new executive role of chief resource officer, working with a team of employees to assure Grant PUD a long-term power supply. The move comes strategically, as Grant PUD evaluates new resources to meet future customer needs, the PUD noted.
Nordt began his career at Grant PUD in 2006 after years as a nuclear engineer, energy trader, analyst and power supply strategy manager for Portland General Electric and later as coordinator of Mid-Columbia River dam operations. He began at Grant PUD as director of power management and then as chief financial officer. Commissioners selected him as general manager in June 2016.
APPA, Others Ask Court To Reject Petitions, Uphold FERC Orders 872, 872-A
December 9, 2021
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
December 9, 2021
The American Public Power Association joined other power industry groups in filing a joint brief in the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit, asking the court to deny petitions challenging Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) orders that revised FERC’s regulations implementing the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act of 1978 (PURPA).
The petitions, filed by the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) and a coalition of renewable energy and environmental groups, seek to vacate FERC orders 872 and 872-A.
The groups joining APPA in the Nov. 22 filing are the Edison Electric Institute, the National Rural Electric Cooperative Association, and the Large Public Power Council. APPA and the other trade groups are intervenors in the appeal in support of FERC, which filed a brief defending its orders in October 2021.
Under PURPA, electric utilities are required to purchase power produced by certain qualifying facilities (QFs) defined in the statute.The rates for these purchases are not to exceed the cost that a utility would have otherwise paid to generate or purchase the power – what FERC calls “avoided cost.” Avoided cost rates are generally set by state or local utility regulators.
Issued in July 2020, FERC’s Order No. 872, among other things, granted greater flexibility to state regulatory authorities in establishing avoided cost rates for QF purchases, both inside and outside of the organized electric markets, providing relief to utilities that have argued for years that some state-set avoided costs had become higher than the wholesale electric costs available to them. The rule also gave states the ability to require that energy rates, but not capacity rates, vary during the term of a QF contract.
Order 872 also modified the “one-mile rule” that FERC had long applied in determining whether a generating resource satisfies the 80 megawatt (MW) limit for one category of qualifying facilities – small power production QFs. The 80 MW limit encompasses all facilities located at the same site, and FERC’s one-mile rule provided that facilities located more than a mile apart were deemed to be located at separate sites. Some utilities had alleged that developers of renewable energy projects used the rule to avoid size limitations on QF projects by disaggregating large projects into smaller components and spacing the components to take advantage of the bright line one-mile rule.
Order 872 also reduced the size threshold that FERC applies in assessing whether a QF has nondiscriminatory access to organized power markets. Under amendments added to PURPA in 2005, utilities can ask to be relieved of the obligation to purchase power from QFs that have nondiscriminatory access to certain power markets. Prior to Order No. 872, FERC presumed that QFs smaller than20 megawatts (MW) lacked nondiscriminatory access to power markets, but FERC’s revised rules lowered the threshold to 5 MW for small power production QFs,, but not cogeneration, facilities.
FERC affirmed Order No. 872 in November 2020 in Order No. 872-A.
In their recent brief to the court APPA and its joint intervenors argued that FERC’s orders “were designed to continue encouraging certain power production addressed in PURPA, while ensuring that customers realize the benefits of the recent growth in renewable generation in the United States without paying above-market rates for that privilege.”
The petitioners “nonetheless cry foul, insisting that the Commission’s Orders will harm the environment and the renewables industry,” the intervenors wrote. “But in truth, their primary concern is preserving an obsolete regulatory framework that has morphed into an arrangement that consistently awards ‘qualifying facilities’ (‘QFs’) with above-market rates for the energy they produce, to the ultimate detriment of energy consumers,” they said.
The petitioners “paper over the fact that the practical effect of adopting their theories would be to extend them a further (decades-long) subsidy financed on the backs of utility customers, including those in rural areas and many who can scarcely afford that burden.”
In support of their position on FERC’s revisions to its avoided costs rate rules, the intervenors argued that FERC did not violate PURPA’s command to “encourage” QFs because the law does not call for the encouragement of QF development without constraint. Rather, the intervenors said, the “statute reflects a balancing of interests, including certain limits on the degree of such encouragement, such as the command that QF prices not exceed a utility’s avoided costs.”
“Petitioners wrongly read PURPA’s ‘encouragement’ clause as a one-way ratchet under which every aspect of every Commission action, taken in isolation, must prefer QF developers over other interests,” the intervenors wrote.
With respect to the “one-mile rule,” the intervenors argued that FERC “reasonably reformed” the rule “to curtail attempts by developers of oversized projects to garner unwarranted QF certification at the expense of consumers.” And in arguing that FERC’s reforms were not supported by the record, the “Petitioners ignore numerous examples of abuse provided by commenters and credited by the Commission,” the intervenors said.
The intervenors also supported FERC’s adjustment of the threshold for presumed nondiscriminatory access to wholesale electric markets from 20 MW to 5 MW, saying the agency’s decision was reasonable.
“Petitioners’ scattershot complaints about FERC’s rationale evince a misunderstanding of what the agency actually said and did,” the intervenors wrote. “In any event, QF developers who are unsatisfied with the revised rule are free to present evidence to overcome the 5 MW presumption.”
The intervenors also dismiss the petitioners’ challenge to FERC’s order as a violation of the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA). APPA and the other intervenors disputed the petitioners’ standing to raise the NEPA claims, while also contending that the challengers’ NEPA arguments failed on the merits.
The intervenors argued that the petitioners’ claims are “meritless” and the court should not grant the requested relief. But if the court does find fault with FERC’s orders, it should not vacate the orders altogether. Rather, the intervenors argued, the court should “remand without vacatur because any such errors can be corrected on remand and because the disruptive consequences of vacatur would be severe.”
The intervenors also argued that the challenged provisions of Order 872 are “sufficiently separable that vacatur should be determined separately for each.” The court “should not invalidate important parts of the rule that no party challenged,” the intervenors wrote.
DOE Study Demonstrates Hydropower’s Ability To Support Grid Reliability
December 9, 2021
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
December 9, 2021
Hydropower can be a valuable resource in maintaining bulk power system reliability, according to a new report from the Department of Energy’s (DOE) HydroWIRES initiative.
HydroWIRES was launched in April 2019 by the DOE’s Water Power Technologies Office to understand and improve the contributions of hydropower and pumped storage hydropower (PSH) to reliability, resilience, and integration in the electric system.
The study analyzed the role of hydropower over a range of extreme events using a combination of historical data and simulation-based analysis.
The study looked at two main categories of events: the sudden loss of large generation assets and changes in net load due to extreme weather such as heat waves and cold snaps.
The scenarios used to evaluate hydropower’s role during extreme events were applied only to the Western Interconnection where hydropower constitutes between 20 and 25 percent of generation capacity.
The study found that hydropower could be critical in stabilizing the Western Interconnection after a sudden loss of generation. Historical data and simulation showed that hydropower is a major resource for inertial and governor response during extreme events. Specifically, the study found that hydropower facilities contribute between 30 and 60 percent of governor response to help stabilize system frequency after an outage.
Hydropower facilities also have significant reactive power capability that can help maintain voltage stability during extreme events, the study found. And while coal and nuclear plants can also provide reactive power, hydropower, like gas-fired plants, do not always operate at full power, enabling them to provide more reactive power support when needed. The study showed that hydropower is a major source of reactive power under all seasonal, loading, and water availability conditions.
The study also found that hydropower’s storage capability and dispatch flexibility are critical to ensuring system reliability during extreme weather events. Simulations of periods of extreme weather when wind and solar generation were significantly depressed, even though the impact on system load was not extreme, showed that hydropower resources were able to fill in energy and capacity gaps.
At least 40 percent of the nation’s hydropower resources are pumped storage and peaking or reservoir hydropower plants that can store water to produce electricity at times of greatest need. At least 18 percent of hydropower resources are run-of-river plants.
During a multi-day cold wave scenario, hydropower resources’ long-term storage capability was key in ameliorating the situation, the study found. In both historical and simulated scenarios, hydropower can contribute “significantly to grid reliability and resilience during extreme events,” the study found.
“The analyses in this study suggest that as the magnitude and frequency of extreme and stressful grid conditions increase, hydropower will continue to play a vital role in power system reliability and resilience,” the report’s authors concluded, adding, however, that “more work needs to be done to fully assess the role of hydropower under all potential combinations of future grid states and extreme events.”
Power Plant Coal Stockpiles Fall To Lowest Levels Since 1978: EIA
December 8, 2021
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
December 8, 2021
Coal stockpiles at electric power plants are at their lowest levels since 1978, according to the Energy Information Administration (EIA).
Stockpiled coal dropped to 80 million metric tons in September, their lowest level since March 1978 when stockpiles hit 77 million metric tons, according to EIA data.
The federal agency attributed the decline to two factors: less coal is needed as coal plants continue to retire and increased generation by coal plants over the summer reduced coal inventories.
In 2019, Moody’s Investors Service projected that utility demand for coal would decline significantly between 2020 and 2030, reducing coal-fired generation to as little as 11 percent of overall U.S. power generation, down from 27 percent in 2018.
Last summer, Moody’s predicted coal company earnings would fall by 50 percent in 2020 because of weak fundamentals and the effects the COVID-19 economic slowdown. The ratings agency also predicted a 25 percent drop in thermal coal production in 2020.
Coal plant operators typically stockpile more coal than they can burn in a month. Generating plants consume the most coal during the summer and winter months, causing stockpiles to drop to their lowest levels in the spring and fall and prompting generators to build back their reserves. However, physical delivery constraints in the supply chain can limit how quickly coal generators can increase their stockpiles, the EIA noted.
Nonetheless, coal stockpiles at generating plants, as measured by the “days to burn” metric, remain within recent historic parameters, the EIA said. “Because of less coal consumption as well as coal capacity retirements over the past three years, the days of burn of U.S. coal remain within the typical range, even though total stocks are low,” the EIA said.
For bituminous coal plants, which are mostly in the eastern United States, the average number of days of burn was 88 days in September, a slight increase from the 86 days of burn recorded by the EIA in August. The average number of days of burn for subbituminous units, which are mostly in the western United States, was 82 days in September 2021, the EIA noted.
The EIA, noting the long-term trend of declining coal consumption, also said many U.S. coal mines have begun to close. That trend, combined with supply chain disruptions, has created some concerns about the ability of coal-fired generators to replenish stockpiles to last through the winter.
Grid operators are, however, closely monitoring coal inventories. As an example, the EIA cited temporary changes taken by the PJM Interconnection regarding minimum inventory requirements to provide more flexibility for coal-fired generators.
